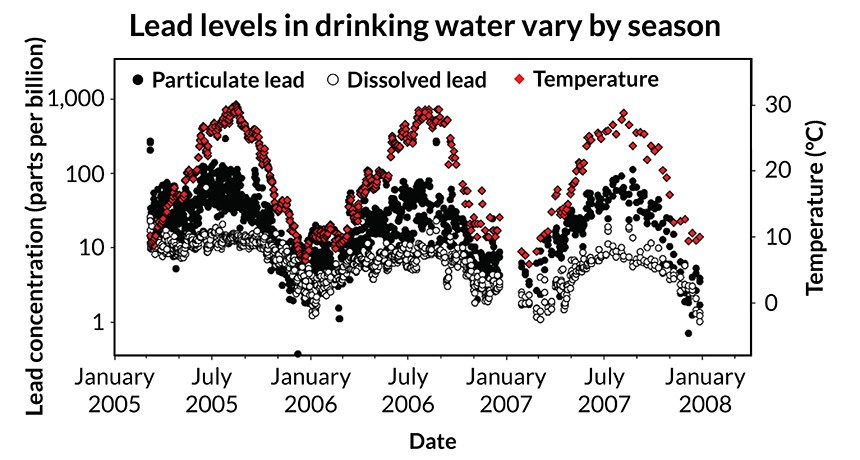
When measuring lead in water, check the temperature
Science News, May 2016Lead contamination in drinking water can change with the seasons. Tracking lead levels in water pipes over several months, researchers discovered three times as much dissolved lead and six times as much undissolved lead in summer than in winter. The finding could help improve water testing, says study coauthor Sheldon Masters, an environmental engineer at Virginia Tech and Corona Environmental Consulting in Philadelphia.