One of Earth’s missing minerals found locked inside meteorite
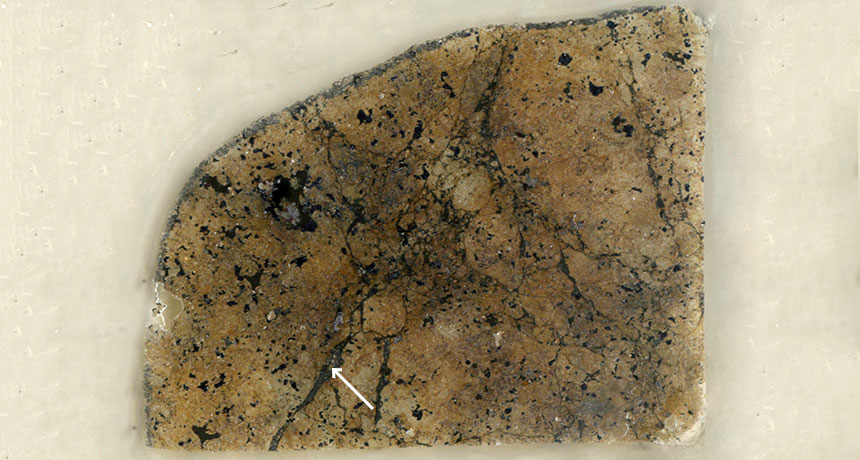
Science News, March 2016The last of a group of dense minerals that make up much of Earth’s crust and upper mantle has been found tucked inside a meteorite that slammed into Australia 135 years ago. The newly discovered mineral, a variety of majorite, is potentially abundant in sinking tectonic plates and could help illuminate the behavior of the deep Earth, its discoverers say.