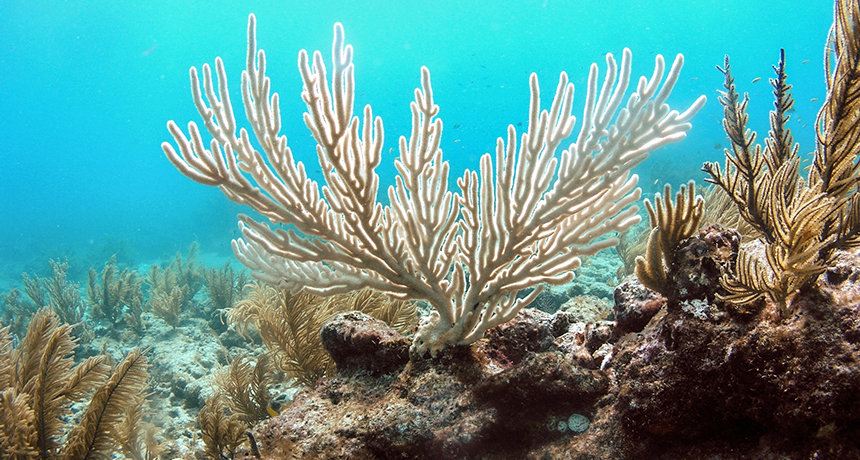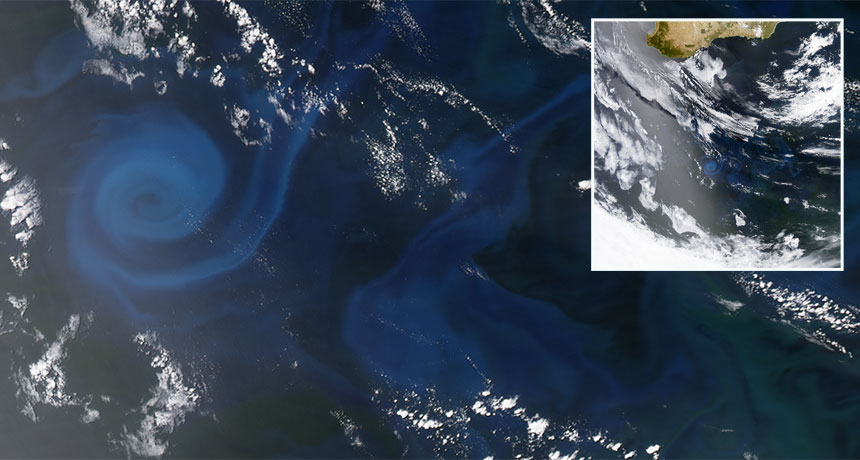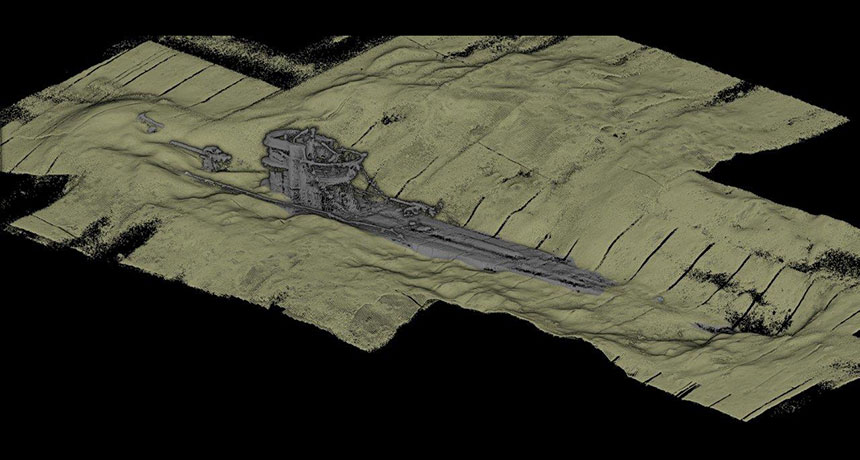
Gulf oil spill could hasten corrosion of shipwrecks
Science News, February 2016Lingering oil from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill could hasten the destruction of historical shipwrecks in the Gulf of Mexico. Tracking the activities of metal-corroding microbes, researchers found that oil mixed into seawater roughly doubled the amount of observed metal corrosion. The scientists reported their findings February 22 at the American Geophysical Union’s Ocean Sciences Meeting.
Adapted for Science News for Students.