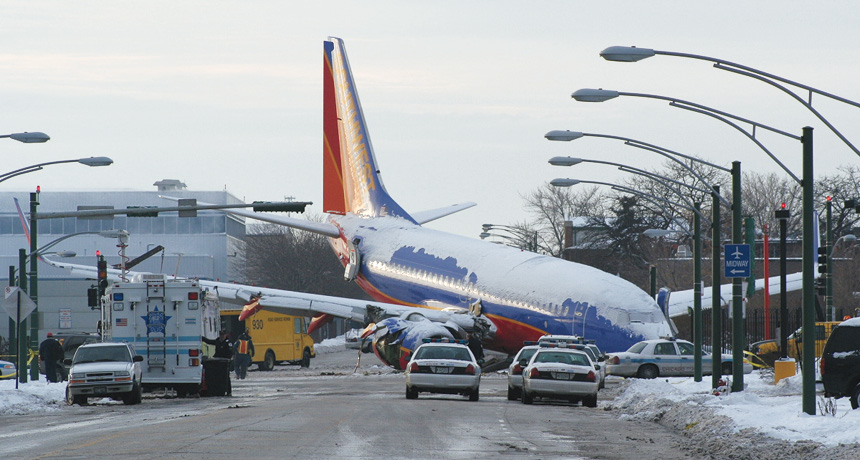

Winter storms 24 times as deadly as estimated
Science News, March 2015Jack Frost’s fury is deadlier than a major report implies, new research suggests.

Jack Frost’s fury is deadlier than a major report implies, new research suggests.
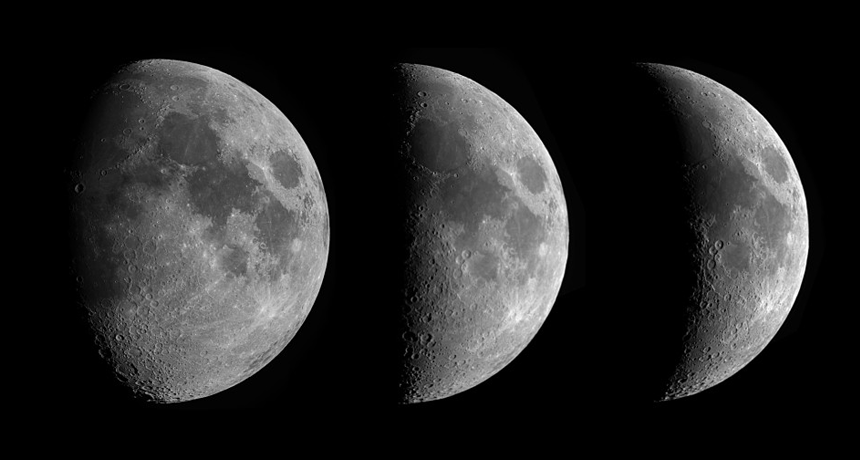

The Earth and moon’s celestial dance was a lot wilder during the pair’s youth. By simulating the early moon’s orbit, researchers have reconstructed what the moon’s phases would have looked like during the solar system’s early years. The result, presented online March 10 at arXiv.org, reveals a moon that alternated rapidly between its sunlit and shadowy sides and bounced like a ball toward and away from Earth.
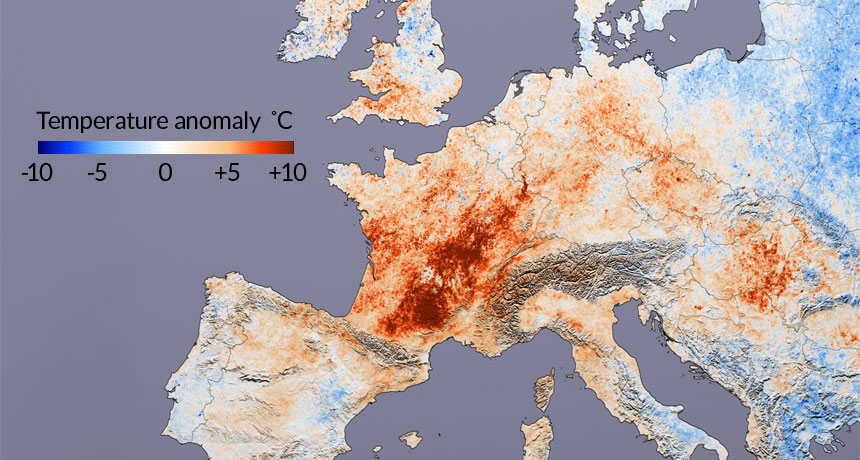
Sweltering summertime heat waves are on the rise across the Northern Hemisphere because of atmospheric changes brought on by Arctic warming, new research shows.
Adapted for Science News for Students.
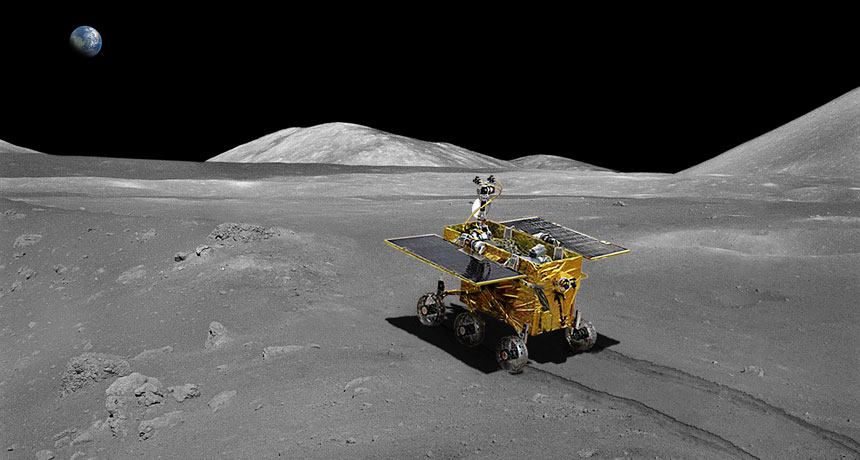
Radar waves beamed into the moon’s surface by China’s Yutu rover have revealed nine distinct subsurface layers directly beneath the rover’s landing site in the Sea of Rains. The multitude of rocky layers suggests that the moon has a more storied geological history than once thought, researchers report in the March 13 Science.
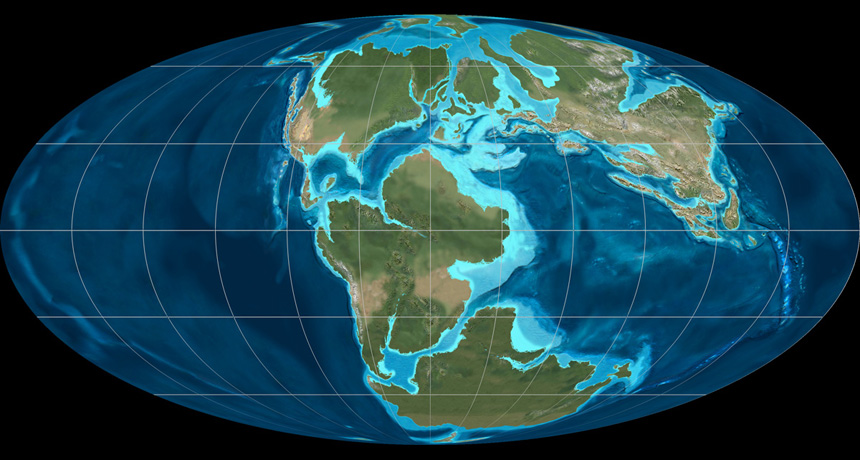
Pangaea’s breakup may have been an outside job. A reexamination of tectonic movements 200 million years ago suggests that the supercontinent was pulled apart by shrinking of the forerunner to the modern Indian Ocean. The new work, presented online February 27 in Geology, signals that scientists may have to rethink Pangaea’s demise, says geologist Stephen Johnston of the University of Victoria in Canada, who was not involved with the research.
Adapted for Science News for Students.
Lightning bolts that flash and clash high above erupting volcanoes can forge flying ash into glass, new research finds. The mechanism could explain the origins of odd microscopic glass beads found embedded in ash deposits, the researchers report online February 27 in Geology.
Adapted for Science News for Students.
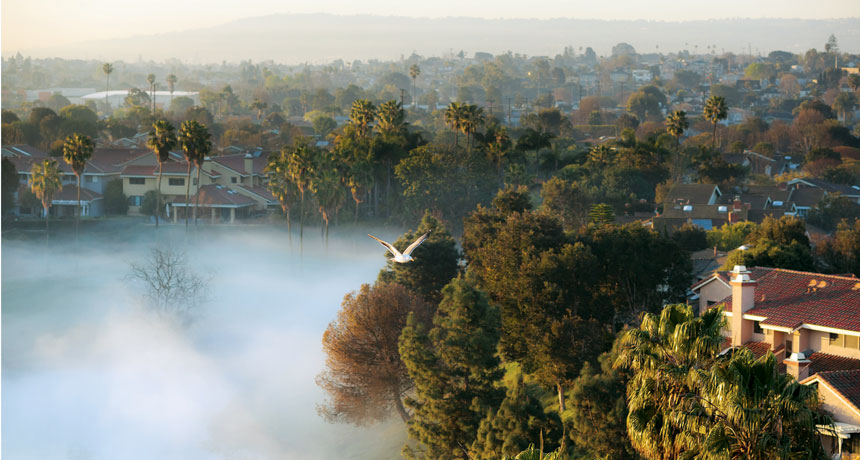

Morning fog along parts of coastal Southern California is disappearing due to nearby urbanization, new research suggests.
Adapted for Science News for Students.
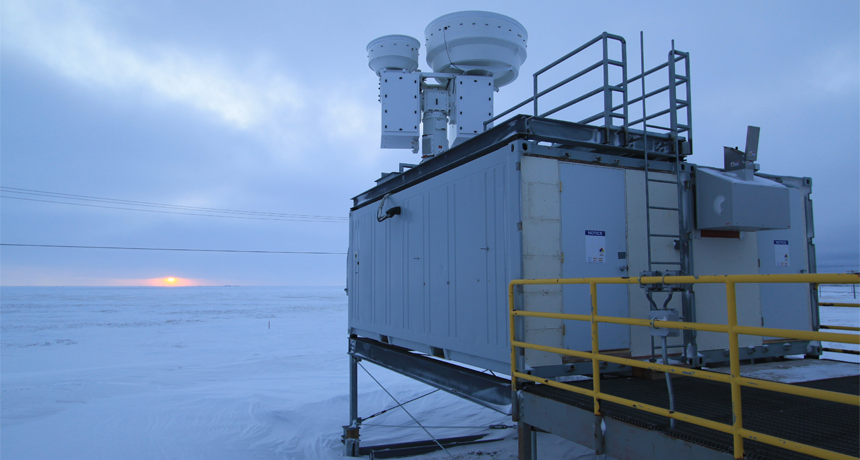

For the first time, scientists have witnessed a direct connection between rising levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide and an increase in the amount of thermal radiation striking Earth’s surface. The work affirms a cornerstone of the theory that humans have contributed to worldwide warming in recent decades, the researchers report online February 25 in Nature.
Adapted for Science News for Students.
Roughly 90 percent of an iceberg’s volume hides beneath the waves. But every so often an iceberg’s underbelly makes an appearance above the waterline.
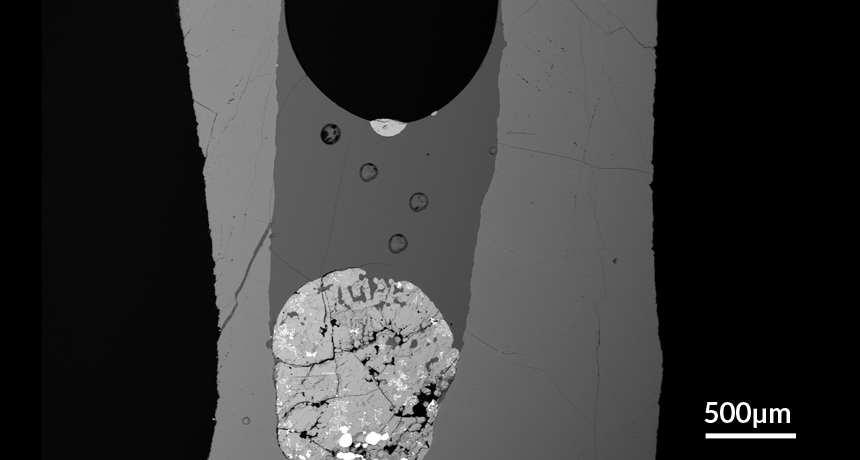
Dense mixes of sulfur and metals such as gold and copper can catch a lift to the top of magma reservoirs on the undersides of rising steam bubbles, new research suggests.