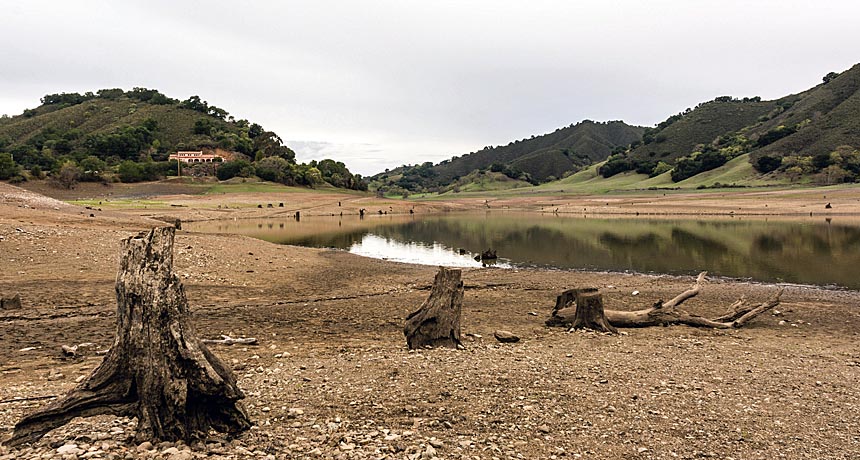
Stalled global warming linked to North American drought
Science News, January 2015The extreme winds blamed for putting the brakes on global warming may also have contributed to the record-setting drought currently parching the southwestern United States, suggests new research presented January 5 at the American Meteorological Society’s annual meeting.