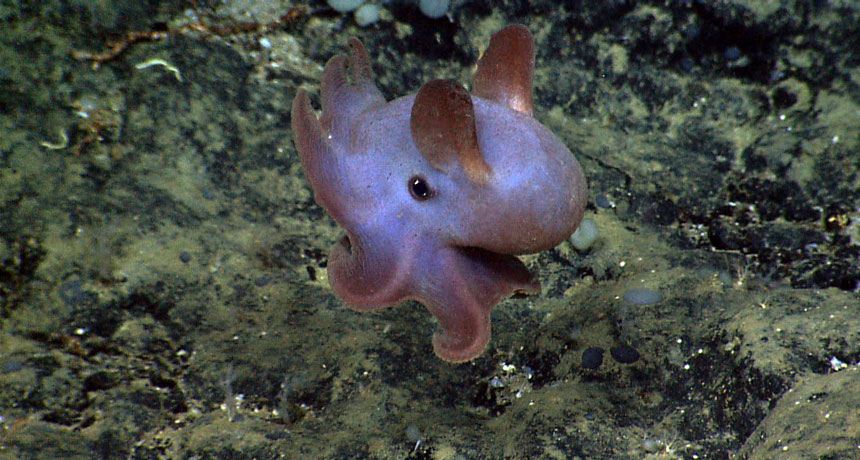

Atlantic monument is home to unique and varied creatures
Science News, October 2016Two stretches of ocean about 210 kilometers southeast of Cape Cod have become the Atlantic Ocean’s first U.S. marine national monument.

Two stretches of ocean about 210 kilometers southeast of Cape Cod have become the Atlantic Ocean’s first U.S. marine national monument.
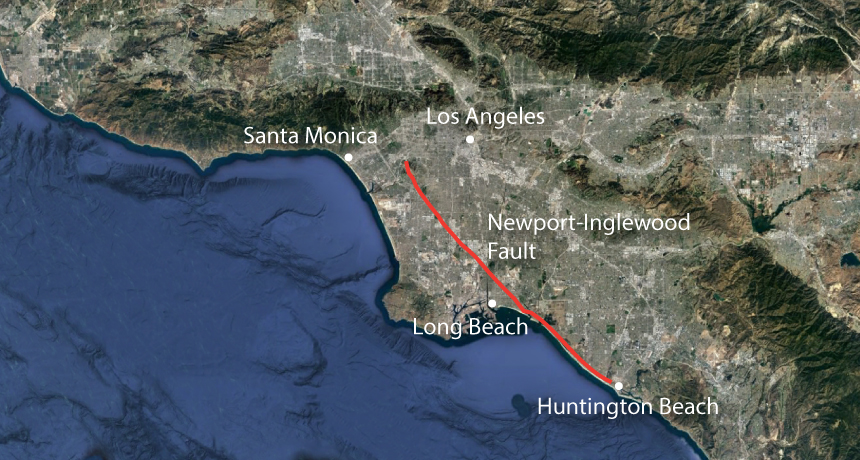
Mysterious earthquakes rattle deep beneath Southern California.

Motors too small to see with the eye may soon have the power to drive innovations in chemistry, biology and computing. Three creators of such nanoscopic machines were honored October 5 with the Nobel Prize in chemistry.
Co-written with Tina Hesman Saey. Adapted for Science News for Students.

A period of skyrocketing global temperatures started with a bang, new research suggests.

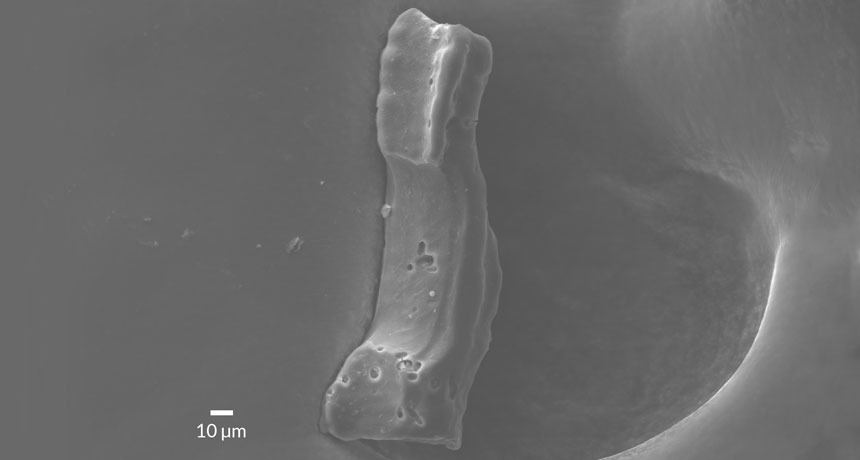
Life on Earth got into the shell game more than 200 million years earlier than previously thought.
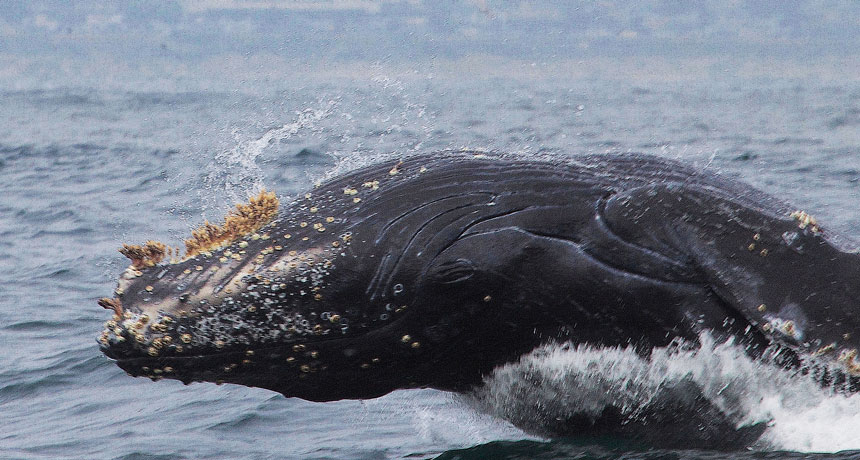

Barnacles can tell a whale of a tale. Chemical clues inside barnacles that hitched rides on baleen whales millions of years ago could divulge ancient whale migration routes, new research suggests.
Methane wasn’t the cozy blanket that kept Earth warm hundreds of millions of years ago when the sun was dim, new research suggests.
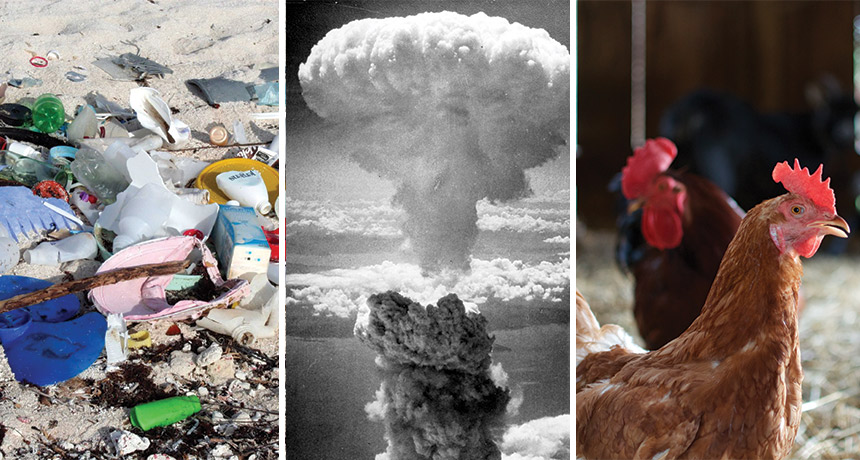

Humankind’s bombs, plastics, chickens and more have altered the planet enough to usher in a new chapter in Earth’s geologic history. That’s the majority opinion of a group of 35 experts tasked with evaluating whether the current human-dominated time span, unofficially dubbed the Anthropocene, deserves a formal place in Earth’s geologic timeline alongside the Eocene and the Pliocene.

A natural ally against global warming may provide far less aid than previously hoped.
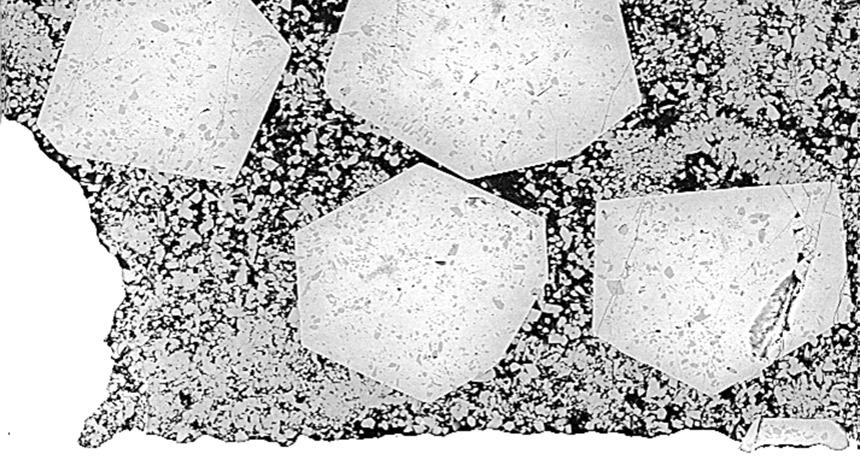
New experiments have re-created the genesis of Earth’s first continents.