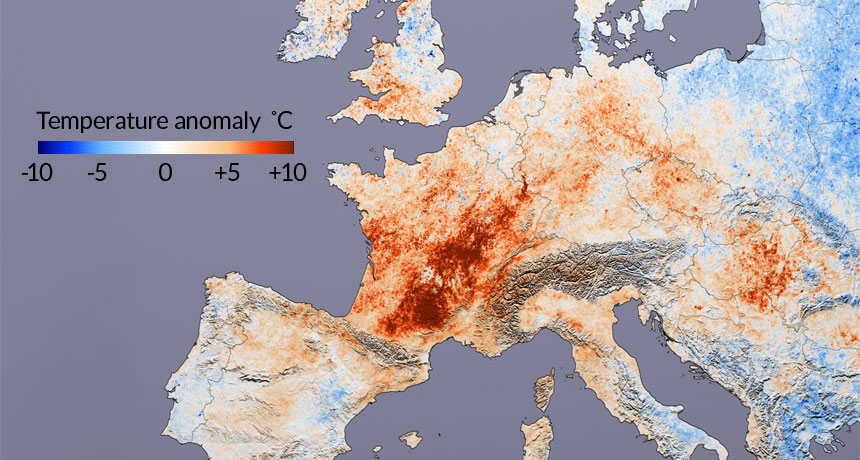
Arctic warming bolsters summer heat waves
Science News, March 2015Sweltering summertime heat waves are on the rise across the Northern Hemisphere because of atmospheric changes brought on by Arctic warming, new research shows.
Adapted for Science News for Students.