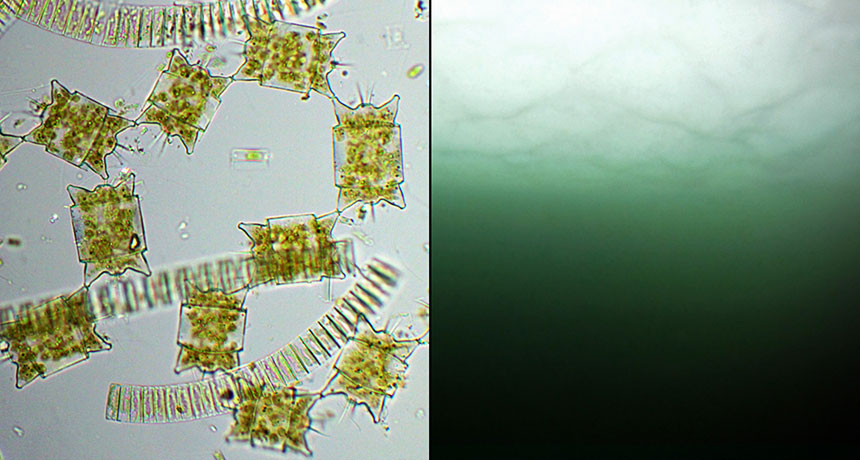
Thinning ice creates undersea Arctic greenhouses
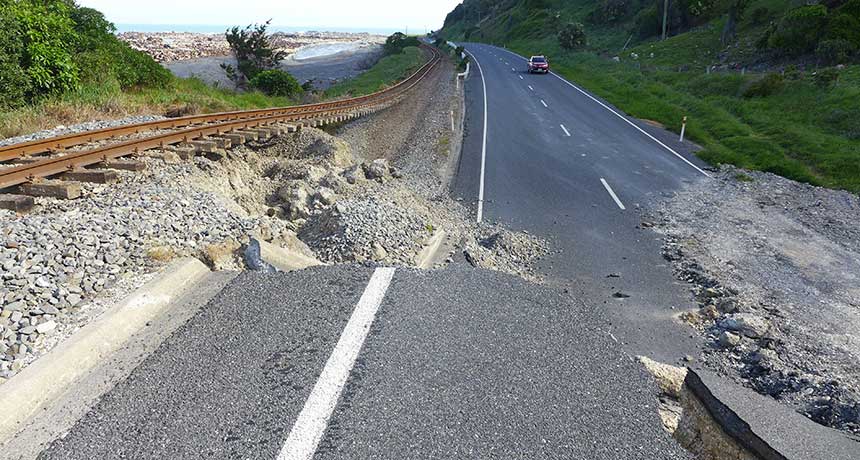
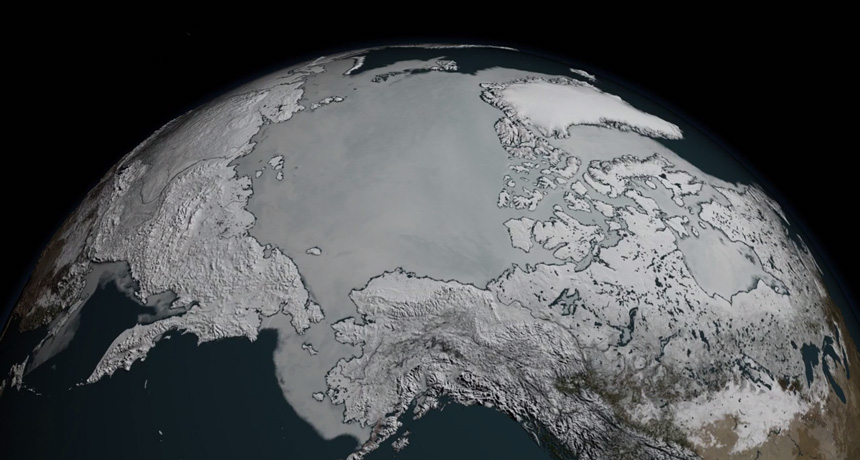
Science News, March 2017Sea ice skylights formed by warming Arctic temperatures increasingly allow enough sunlight into the waters below to spur phytoplankton blooms, new research suggests. Such conditions, probably a rarity more than two decades ago, now extend to roughly 30 percent of the ice-covered Arctic Ocean during July, researchers report March 29 in Science Advances.






